"Exploring the Power and Purpose of Parametric EQ in Music Production and Mixing"
Equalization, commonly known as EQ, is an essential tool for any audio engineer or music producer. It helps to sculpt and shape the tonal balance of individual tracks and the overall mix. One of the most commonly used types of EQ is the parametric EQ. In this blog, we will explore what a parametric EQ is, how to use it, and its purpose in a mix and on individual tracks.

What is a Parametric EQ?
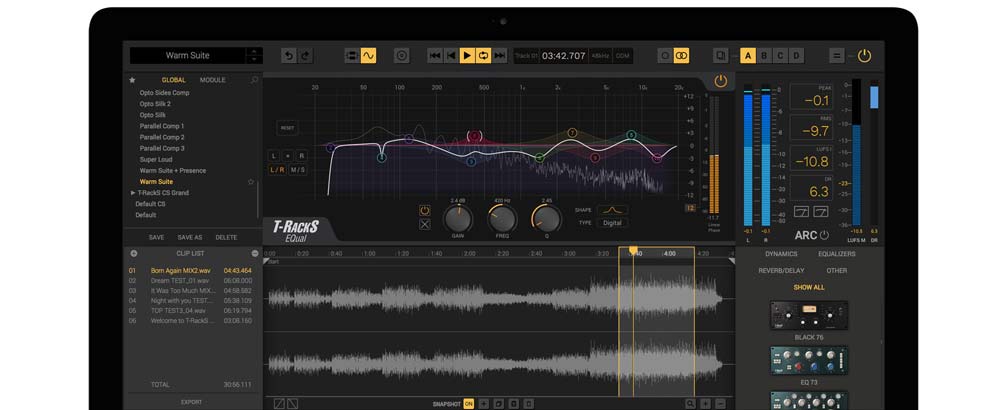
A parametric EQ is a type of equalizer that allows for precise control over the frequency, bandwidth, and level of the audio signal. It is called "parametric" because it allows you to adjust parameters such as center frequency, Q-factor, and gain. Unlike a graphic EQ that has fixed frequency bands, a parametric EQ allows you to select any frequency range within the EQ's overall range and adjust the amount of boost or cut in that range.
How to Use a Parametric EQ?
Using a parametric EQ is relatively easy once you understand its controls. Here are the primary controls of a parametric EQ:
- Frequency Control: This allows you to choose the center frequency you want to adjust. You can use this to target specific frequencies or ranges of frequencies that need boosting or cutting.
- Q Control: The Q-factor, or quality factor, determines the bandwidth or range of frequencies that will be affected by the EQ. A narrow Q value will affect a smaller range of frequencies, while a wider Q value will affect a broader range.
- Gain Control: This is used to boost or cut the selected frequency range.
When using a parametric EQ, it's best to start with a neutral or flat EQ curve and make subtle adjustments. Too much boosting or cutting can result in a harsh or unnatural sound. You can make small adjustments, listen to the changes, and make further adjustments until you achieve the desired sound.
Purpose of a Parametric EQ in a Mix and on Individual Tracks
The primary purpose of a parametric EQ is to shape the tonal balance of individual tracks and the overall mix. It can be used to remove unwanted frequencies, boost specific frequencies, or correct any tonal imbalances. Here are some ways in which a parametric EQ can be used on individual tracks:
- Vocals: A parametric EQ can be used to remove unwanted low-frequency rumble or hiss in a vocal track. Boosting the presence range around 2-5 kHz can add clarity and help the vocal cut through the mix.
- Bass: Boosting the low-end frequencies around 60-80 Hz can add warmth and thickness to a bass track. Cutting frequencies in the 200-400 Hz range can reduce muddiness and give the bass more definition.
- Guitar: Depending on the style of music, a guitar track can benefit from different EQ settings. Cutting the low-end frequencies can reduce mud and give the guitar a more defined sound. Boosting the mid-range frequencies around 800-1kHz can add warmth and presence to the guitar.
When it comes to the mix, a parametric EQ can be used to balance the overall tonal balance. Here are some ways in which a parametric EQ can be used in a mix:
- High Pass Filter: Applying a high-pass filter to all tracks except for the bass and kick drum can reduce low-frequency clutter and make the mix sound cleaner.
- Notching: Notching out specific frequencies in individual tracks can help reduce frequency masking and make the mix sound more transparent.
- Mastering EQ: A mastering engineer may use a parametric EQ to make subtle adjustments to the overall tonal balance of the mix. They may also use a parametric EQ to correct any tonal imbalances in the final master.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a parametric EQ in our opinion is a great tool to use to enhance your mixes and individual tracks
-MusicLabz
